Sopranino clarinet  | The sopranino clarinet is the smallest, and therefore the highest of all clarinets. It measures only 25 centimetres, and its body is made of a single piece, either of wood or metal. Its sound, both strident and piercing, is linked to the small size of the instrument. It is so small that the fingers touch once they are placed on this clarinet. The rarity of this instrument is due to its unusual use. It was mainly used by Italian bandas for military music. Verdi's Bal Masqué is the most significant piece in the classical repertoire of this instrument. This clarinet seems to be given pride of place by contemporary composers for its sound, like Gilbert Amy with "Espace déployé". |
Key: Ab
Soprano clarinet in E flat | A little larger than the sopranino, this clarinet is much more common than its little sister. Just look at the offer of the factors to see it immediately. Depending on the models, the body is either in one piece or in two parts. Like most clarinets, this model is called transposing. That is to say, when playing a written C, the real note is an E flat located a minor third above it. The soprano clarinet in E flat is also called a piccolo clarinet because of its high register. Although difficult to control, this register is often described as blatant, ironic or even sarcastic. His character is particularly evident in the pieces "Till the Mischievous" (Richard Strauss) or "The Fantastic Symphony" (Berlioz). Its medium and low registers are better suited to melancholic and tenebrous passages. Made popular by orchestras, this clarinet made its first appearance in the orchestra at the end of the 19th century. She will only settle there definitively thanks to composers from the French school such as Roussel, Milhaud or Ravel. |
Key: E flat Clarinet in D
| Although better represented by the factors than the sopranino in A flat, the clarinet in D remains quite rare. This clarinet is now used almost exclusively for the performance of Molter's concertos. Its tone is softer than that of E flat in the low register, and it offers a seductive high register. Some of Richard Strauss' and Stravinsky's pieces include features written for this instrument, but instrumentalists very often prefer to transpose them for the soprano clarinet in E flat.
|
Tone: D
Clarinet in C
| Like the clarinet in D, the clarinet in C is rarely used. However, the offer is more extensive than that of the D model, as more and more conservatories are introducing their youngest students to this clarinet. The sound of this instrument is quite aggressive and instrumentalists often prefer to transpose their lines on their B-flat. The repertoire of written pieces using this clarinet is quite extensive, but the main works remain "Le Scare du Printemps" (Stravinsky) and Rossini's operas.
|
Tone: C
Clarinet in B flat B
| By far the most widespread model, the b flat is the reference of the clarinet. Each factor has many models available in beginner, intermediate and professional models. These clarinets are available in plastic, wood/resin powder alloy, wood, and even metal. Some models allow access to the lower E-flat and also have an E-flat lever / the additional E-flat for the left hand Its sound is soft, powerful and brilliant. It is very frequently used as a solo instrument in the orchestra (as in Weber's or Spohr's concertos), where it blends perfectly with woodwinds and strings. It is for this type of clarinet that the vast majority of the pieces in the repertoire are written.
|
Tone: B flat
Clarinet in A
| Despite the slight difference in key (half a tone), the clarinet has its own sound very different from that of B flat. The number of models available for this type of clarinet is very large, suggesting its popularity! Technically, it is a little longer, and therefore requires more air and pressure during emission. This is probably what gives it its soft and penetrating timbre, but also darker than the clarinet so flat. It also seems to have more inertia in attacks and nuances. The clarinet in it is widely used in chamber music, particularly in famous pieces such as "Pièces de Fantaisie" (Schumann), "Quintet for strings and clarinet" (Mozart), or "Sonatas for clarinet and piano" (Brahms).
|
Tone: A
A of basset
| This instrument differs from the clarinet in A by its additional low third. Indeed, while the clarinet in A stops at mid or mid-flat low (depending on the models), this clarinet goes down to the low C. The clarinet "la de basset" is a rare instrument because its repertoire is very limited. It is mainly used for Mozart's pieces (concerto for clarinet and orchestra, quintet for strings and clarinet, and divertimenti). Its range is similar to that of a basset horn, but its morphology and tonality make it more like a clarinet in the (longer). |
Tone: A
Alto clarinet
| The Alto clarinet in E flat has a tone very close to that of the basset horn, but sounds a tone below it It is used mainly in ensembles and harmonies, and has no particular repertoire. The offer of the makers is rather surprising considering the repertoire of the instrument, and its almost exclusive use in Dutch harmonies... |
Tone: E flat
Basset horn
| Also known as the viola clarinet in F, the basset horn is located somewhere between the B-flat clarinet and the bass clarinet. It sounds in the fourth below E flat and resembles a bass clarinet with its curved bell. Invented between 1760 and 1770, this instrument owes its name to the fact that it looked like a horn because of the shape of its bell, and that its register was close to that of the bass. Its sound is very close to the human voice, and is often described as tender and voluptuous. This instrument has been widely used by Mozart, Strauss and Massenet. The most famous pieces written for this instrument are Mozart's concerto for clarinet and orchestra, quintet for strings and clarinet, and divertimenti. His requiem also begins with a solo of two basset horns.
|
Tone: F
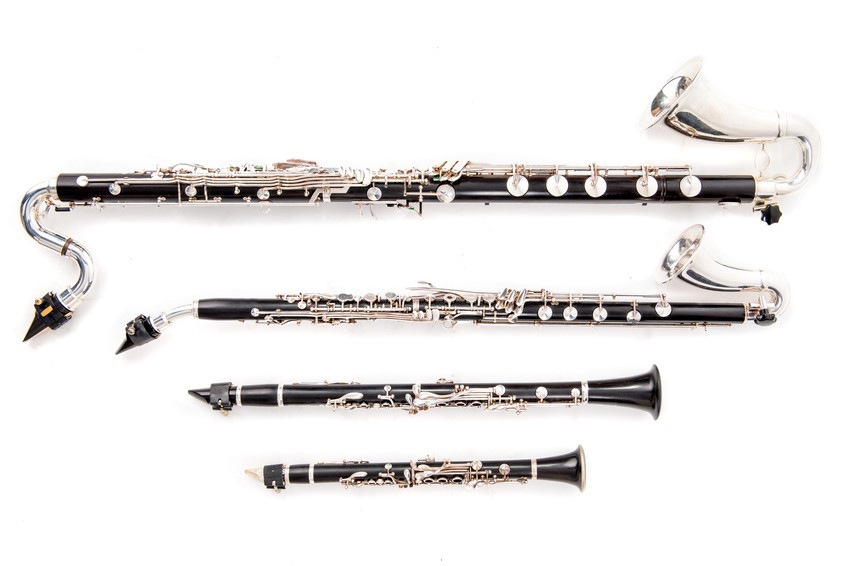
Bass clarinet
| The clarinet bass in B flat sounds exactly one octave below the B flat clarinet. Its main interest lies in its remarkable sound in the low, dark and cavernous bass, sometimes reminiscent of an organ. The midrange register is less timbre, and the treble more violent and less centered than that of the "ordinary" clarinet. There are several types of bass clarinets, but in practice we mainly distinguish between models that allow access to the low E flat (left photo), and those that are able to reach the C (right photo). This instrument was introduced in 1848 by Wagner for his piece Lohegrin, then reused by many others from Verdi to Pierre Boulez.
| |
Tone: B flat
Clarinet against viola
|
This clarinet sounds a fifth below the bass clarinet, an octave below the viola clarinet.
Its low register is very deep, and is often referred to as cavernous or distant. Like its alto sister, the counter viola is mainly used in clarinet ensembles and harmonies. Schoenberg is one of the composers to have written specifically for this instrument. |
Tone: E flat
Contrabass clarinet
|
The contrabass clarinet sounds to the octave below the bass.
Its very deep sound is reminiscent of an organ, but with a lower power. This instrument is rare, and like the contra viola clarinet, remains mainly used as an ensemble of clarinets and harmonies. | |
Tone: B flat |